
Getting the Most from MIN, MINA, and MINX Functions in Power BI for Robust Reporting
Jul 25, 2024
Getting the Most from MIN,
MINA, and MINX Functions in Power BI for Robust Reporting
In today’s blog post, I’ll explore how to effectively
use the MIN, MINA, and MINX functions in Power BI. These functions will enhance
your data models and reports by providing precise calculations for minimum
values and averages, enabling more accurate and insightful data analysis.
When working with Power BI, the Data Analysis
Expressions (DAX) language provides a range of functions for performing
calculations and aggregations. Among these functions, MIN, MINA, and MINX are
essential for statistical analysis and aggregating data. This blog explores
these functions, their usage, and how they can be applied effectively in Power
BI.
MIN Function
The MIN function is used to find the smallest value in a
column or table. It is ideal for numerical data where you need to determine the
minimum value.
Syntax:
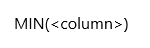
Parameters:
column: The column from which to return the
smallest value.
Example:
Suppose you have a table named Sales with a column SalesAmount.
To find the minimum sales amount, you can use:
dax
MinSalesAmount = MIN(Sales[SalesAmount])
This formula returns the smallest value in the SalesAmount
column.
MINA Function
The MINA function is similar to MIN, but it can handle
non-numeric values as well. It evaluates values as numbers where possible, but
retains text and Boolean values in its calculation. For text, it returns a
minimum based on alphabetical order, and for Boolean values, FALSE is
considered less than TRUE.
Syntax:
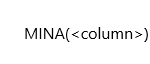
Parameters:
column: The column from which to return the
smallest value, evaluating all values.
Example:
Consider a table EmployeeData with a column EmployeeScore
that contains mixed data types, such as numbers and text. To find the minimum
value, you would use:
dax
MinEmployeeScore = MINA(EmployeeData[EmployeeScore])
This function will compare numbers, text, and Boolean
values in EmployeeScore and return the minimum based on the evaluation.
MINX Function
the MINX function is used in Data Analysis Expressions
(DAX) to return the smallest value of an expression evaluated over a table.
It’s often used in combination with other functions to perform
complex calculations.
Syntax:
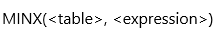
Parameters:
table: A table or table expression over which
the MINX function will iterate.
expression: An expression that is evaluated for
each row in the table.
Example:
Suppose you have a table named Sales with columns
Product, Quantity, and Price. You want to find the minimum value of the total
revenue (which is Quantity multiplied by Price) across all products.Here’s how
you can use the MINX function to achieve this:
Create a new measure in Power BI using the following DAX
formula:
Min Revenue = MINX(
Sales,
Sales[Quantity] * Sales[Price]
)
This measure calculates the total revenue for each row
and then finds the smallest revenue value.
Illustrative Screenshots of MIN, MINA, and MINX Functions in Power BI
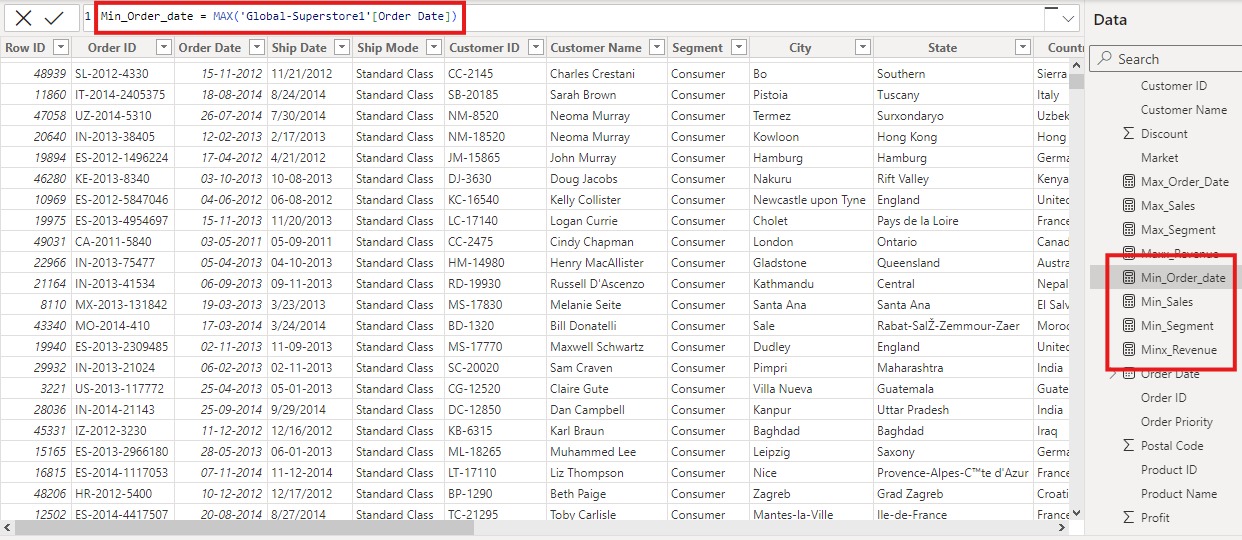
Conclusion
Understanding DAX functions MIN, MINA, and MINX in Power BI is essential for effective data analysis. MIN finds the smallest numeric value, MINA handles mixed data types, and MINX calculates the average of an expression over a table. Mastering these functions enhances your ability to derive valuable insights and create more accurate reports.
For more detailed guidance and in-depth training, visit
our training here.


