
Formatting Dates, Numbers, and Times with the FORMAT Function in Power BI
Aug 09, 2024
Formatting Dates, Numbers, and
Times with the FORMAT Function in Power BI
In today’s blog post, I will explain how to use the
FORMAT function in Power BI. The FORMAT function is a powerful tool that allows
you to format numbers, dates, and other values according to your specific
requirements. This function is particularly useful when you want to present
your data in a more readable and user-friendly format.
What is the FORMAT Function?
The FORMAT function in Power BI is used to convert a
value to text according to a specified format. It is especially handy when you
need to display data in a particular way, such as showing a date in a specific
format or converting a number to a currency format.
The syntax of the FORMAT function is as follows:

- value:
The value you want to format. This can be a number, date, or time.
- format_string: A
string that defines the format you want to apply to the value.
Common Use Cases for the
FORMAT Function
Formatting Dates:
The FORMAT function can be used to display dates in
different formats. For example, if you have a date field that you want to
display as "January 01, 2024," you can use the following expression:
mathematica
FORMAT([Order Date], "MMMM dd, yyyy")
This will format the date as "Month Day,
Year," such as "January 01, 2024."
Formatting Numbers:
If you want to format numbers as currency or
percentages, the FORMAT function is perfect for the job. For example, to format
a number as currency, you can use:
FORMAT([Sales], "Currency")
This will display the sales amount with a currency
symbol, such as "$1,000.00."
Custom Number Formatting:
You can create custom number formats using the FORMAT
function. For instance, if you want to display a number with commas as
thousands separators, you can write:
FORMAT([Sales], "#,##0")
This will display the number 1000000 as
"1,000,000."
Formatting Time Values:
The FORMAT function can also be used to format time
values. For example, to display a time value in the format "hh
AM/PM," you can use:
FORMAT([Time], "hh:mm tt")
This will display the time as "02:30 PM."
Advantages of Using the FORMAT
Function
- Consistency: The FORMAT function
ensures that your data is displayed consistently across your reports.
- Flexibility: You can easily switch
between different formats without altering the underlying data.
- Readability: Properly
formatted data is easier for users to understand and interpret.
Practical Example: Using
FORMAT in a Report
Let’s say you have a sales report that includes order
dates and sales amounts. You want to display the order dates in a "Month
Day, Year" format and the sales amounts as currency. You can achieve this
using the FORMAT function as follows:
mathematica
Formatted Date = FORMAT([Order Date], "MMMM dd,
yyyy")
Formatted Sales = FORMAT([Sales], "Currency")
These calculated columns will make your report more
user-friendly by presenting the dates and sales in a clear, readable format.
Illustrative Example of FORMAT Function
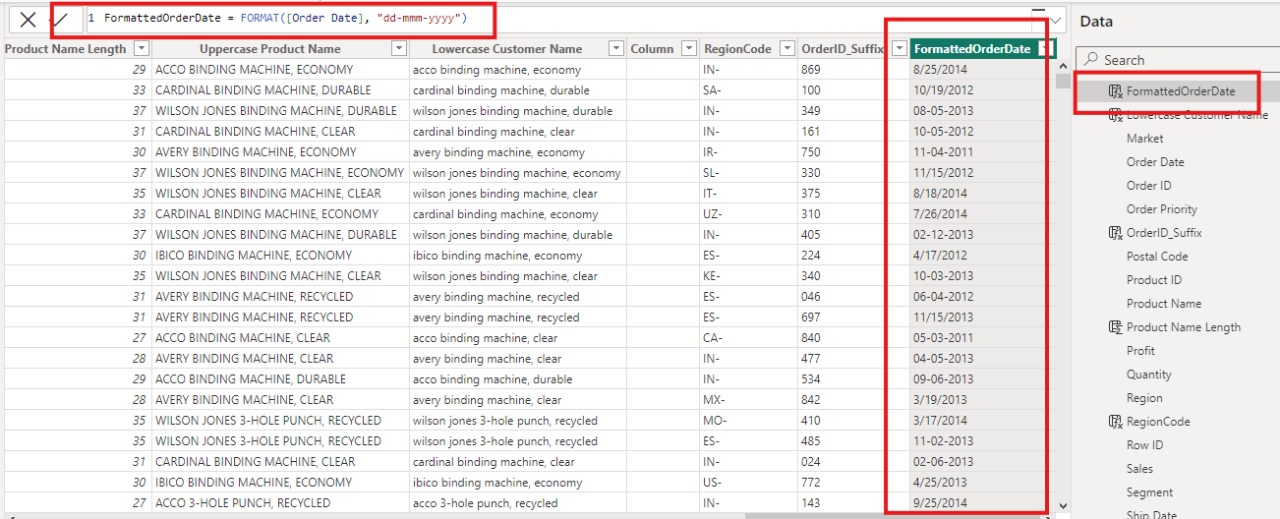 Conclusion
Conclusion
The FORMAT function is a valuable tool in Power BI that
allows you to customize how your data is displayed. Whether you are formatting
dates, numbers, or times, the FORMAT function provides the flexibility you need
to create polished, professional reports. Understanding how to use this
function effectively can significantly enhance the readability and presentation
of your data in Power BI.
For more detailed guidance and in-depth training, visit our training here.

