
Conditional Statements in Power BI: Understanding the IF Function
Jul 26, 2024
Conditional Statements in
Power BI: Understanding the IF Function
In today’s blog post, I’ll walk you through the process
of using the IF function in Power BI. This essential function allows you to
apply conditional logic to your data, enabling you to create more dynamic and
insightful reports by making decisions based on specific conditions.
The IF function is one of the fundamental functions in
Power BI, essential for creating conditional logic in your data models. Whether
you are a novice or an experienced user, understanding the syntax and
capabilities of the IF function can significantly enhance your data analysis
and reporting capabilities. In this blog, we'll delve into the syntax of the IF
function and explore its importance in Power BI.
Understanding the IF Function
The IF function in Power BI is used to perform logical
tests and return different values based on whether the test evaluates to TRUE
or FALSE. This function is particularly useful for creating new columns,
measures, or tables based on conditional logic.
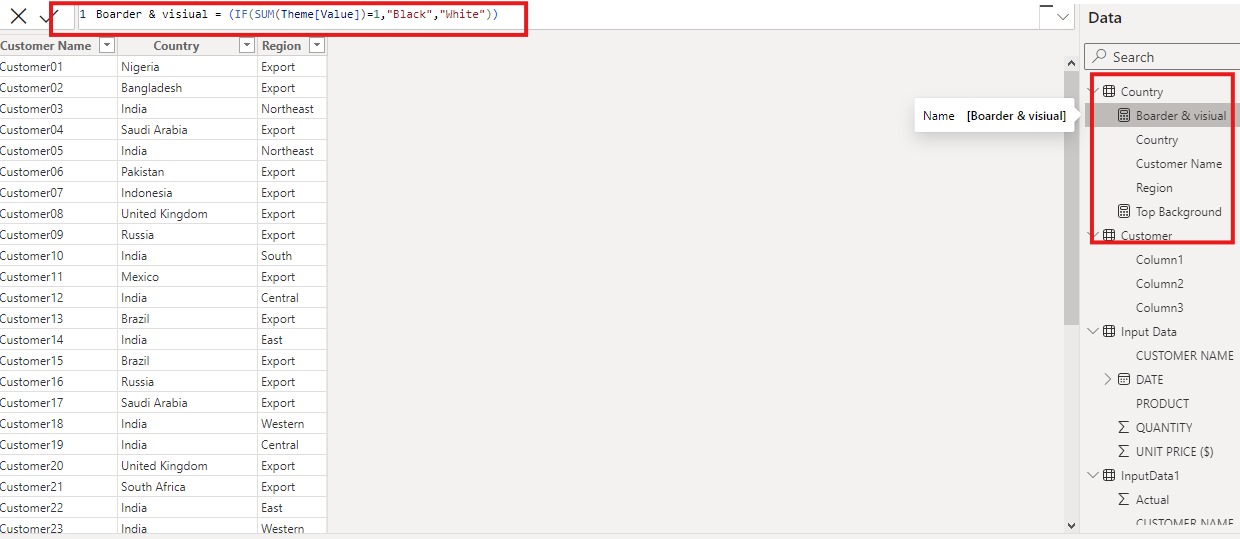
Syntax of the IF Function
The basic syntax of the IF function is as follows:

Here’s a breakdown of each component:
- logical_test: This
is the condition you want to test. If the condition is TRUE, the function
will return the value specified in the
parameter. - value_if_true:
This is the value that will be returned if the
evaluates to TRUE. - value_if_false: This
is the value that will be returned if the
evaluates to FALSE. This parameter is optional; if omitted, the function will return BLANK() when the condition is FALSE.
Key Points to Remember
Conditional Logic: The IF function is crucial for applying
conditional logic to your data. It allows you to dynamically change the values
based on the data context, making your reports more interactive and insightful.
Nested IF Statements:
You can nest multiple IF statements within each other to handle more complex
conditions. However, it's essential to manage these nested statements carefully
to maintain readability and performance.
Performance Considerations:
While the IF function is powerful, excessive use of complex conditional logic
can impact performance. It's advisable to optimize your logic and avoid
unnecessary nesting where possible.
Combining with Other Functions:
The IF function can be combined with other DAX functions like AND, OR, SWITCH,
and more to create intricate conditional expressions. This combination enhances
the flexibility and power of your calculations.
Handling Missing Values:
When dealing with data that may have missing values, using the IF function to
handle these cases can improve the robustness of your reports. You can specify
default values or calculations for scenarios where data might be incomplete.
Debugging and Testing:
When creating complex IF statements, always test your logic thoroughly. Use
Power BI's debugging tools and check intermediate results to ensure your
conditional logic behaves as expected.
Conclusion
The IF function is a versatile tool in Power BI that enables you to apply conditional logic to your data models efficiently. By mastering its syntax and understanding its best practices, you can enhance your data analysis capabilities and create more dynamic and insightful reports.
For more detailed guidance and in-depth training, visit our training here.

